Securing the Autonomous Future: Why Identity is Key to Agentic AI
Agentic AI is more than a buzzword or trend. In fact, a recent article in the Harvard Business Review suggests that “Agentic AI systems promise to transform many aspects of human-machine collaboration, especially in areas of work that were previously insulated from AI-led automation, such as proactively managing complex IT systems to pre-empt outages; dynamically re-configuring supply chains in response to geopolitical or weather disruptions; or engaging in realistic interactions with patients or customers to resolve issues.
But what does it even mean?
Before we dive into the security aspects, let's get a clear understanding of what Agentic AI actually is. Agentic AI is a framework for allowing AI agents to collaborate with each other and other humans to accomplish a goal. As Brian shared, AI agents are autonomous systems that “perceive their environment via APIs or other inputs, make decisions based on goals or objectives, and take actions to try to reach that goal.” Built on Large Language Models, agentic AI is much more powerful than traditional automation since AI agents can have their own goals, work autonomously, access tools and collaborate, similar to how a human team would interact to solve a complex problem.
Agentic AI in Identity Security

Full automation is the great white whale of identity security – that ideal future state that enables you to achieve operational efficiency and finally set your teams free from manual processing of provisioning/deprovisioning, logging, and monitoring. Agentic AI can help you achieve this goal.
So what does that look like?
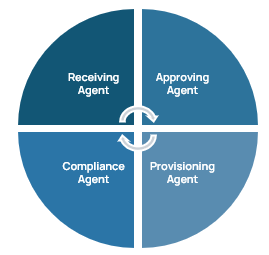
Brian shared an example of how AI agents might work together in practice.
“Let’s consider an access request workflow to allow a user privileged access to the corporate payroll system. You could have 4 agents working together, each with their own particular skills, making decisions on their own with specialized instructions.
- A Receiving Agent would receive the user’s access request and start the process.
- An Approver Agent then validates it against access management policy to determine if the user should have access.
- A Provisioning Agent provisions access to the payroll solution.
- A Compliance Agent logs and audits the changes and checks for compliance.
In this scenario, these agents work together, autonomously, to securely onboard access with minimal human touch.
The Challenge of Securing Agentic AI
Spiderman put it best when he reminded us that “great power comes great responsibility.” AI has so much to offer as we automate and scale operations, but it comes with inherent risks.
Brian noted that Agentic AI’s risks can be categorized as traditional AI risks, human identity risks, and machine identity risks. “Traditional AI’s risks are fairly well-known – data leakage, prompt injection, and hallucinations. However, because agentic AI can act autonomously and take action - this introduces many additional risks. Autonomous agents behave like both human users and machine identities, giving you risks from both of those areas.
Human Identity Risks

Agents make decisions and access resources like people do (and like with people, this can be a good or bad thing). To mitigate this risk, you have to verify the agent’s identity and ensure that they have appropriate permissions.
Machine Identity Risks

Just like service accounts, AI agents run non-stop, make their own decisions, and take action faster than most humans can react. With so much power and privilege, machine identities require rigorous authentication, monitoring, and lifecycle controls.
Without these strong security measures in place, a rogue AI agent could, for example, access data it wasn’t supposed to and pass it on to another agent or could unintentionally make a configuration change that could expose your data.
Overcoming Agentic AI’s Security Risks
The bottom line is this: AI agents have risks beyond traditional AI because they have both human and machine traits. For this reason, our security strategy must include solutions that address human and machine identity challenges.
Based on his experience, Brian shared his strategy for securing agentic AI. “To secure them properly, we need to apply and evolve our identity controls, including:
- Role-based access: AI agents should only have the minimum permissions they need.
- Entitlement management: Clearly define and track what agents are allowed to do.
- Lifecycle management: Agents should be verified, onboarded, monitored, and decommissioned just like employees or service accounts.
The truth is, there really is no escaping AI technology. AI agents are rapidly becoming a necessary component of workplace productivity. If you fail to apply identity governance to these AI tools, you’re going to expose your organization to serious risk.
Preventing an AI Identity Crisis
So how can you prevent an AI identity crisis?
Brian explained, “securing agentic AI begins with identity — and identity needs to be front and center as this tech continues to evolve. To meet the need, organizations must deploy modern IGA programs based on best practices and Zero Trust principles.
Interested in learning more about how we can help you secure your autonomous future? Contact KeyData Cyber today for an assessment of your current security architecture and a roadmap to a secure, scalable IAM program.



